NLP
Natural Language Processing
Modern style
What we saw last time
-
classic NLP
- tokens
- NER: Named Entity Recognition
- POS: Part of Speech
- topic modeling
- text classification : sentiment, toxic, category, spam etc
-
Practice on the NYT API to build a dataset and apply classic NLP techniques
Today
-
modern NLP
- embeddings
- LLMs
- RAG
-
Spacy.io for NER and POS and lemmatization
-
Demo with spacy.io
-
Practice on the NYT dataset you built last time to apply classic NLP with Spacy
At the end of this class
You
- understand what embeddings are
- understand what RAG is
- can apply classic NLP techniques to a dataset using Spacy.io
In the News
What caught your attention this week?
Modern NLP - Embeddings
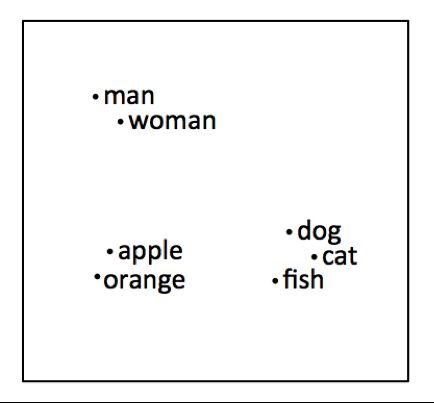
the problem : how to find similar texts ?
In a large corpus how do you find sentences, paragraphs that adresss similar topics ?
Or put differently how to calculate a distance between 2 texts ?
distance
How to calculate a distance between 2 texts so that we can say that
bananais closer toapplethan it is toplane;- the
dog barksis closer to thecat meowsthan it is to theplane takes off, …
Before 2013: counting words and their relative frequencies The method, crude, called tf-idf, worked well for spam detection, requires lots of text pre processing (stopwords, lemmatization, ...). OOV, can't scale to large vocabularies, typo sensitive, etc etc
Word2vec 2013
Thomas Mikolov @Google Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space
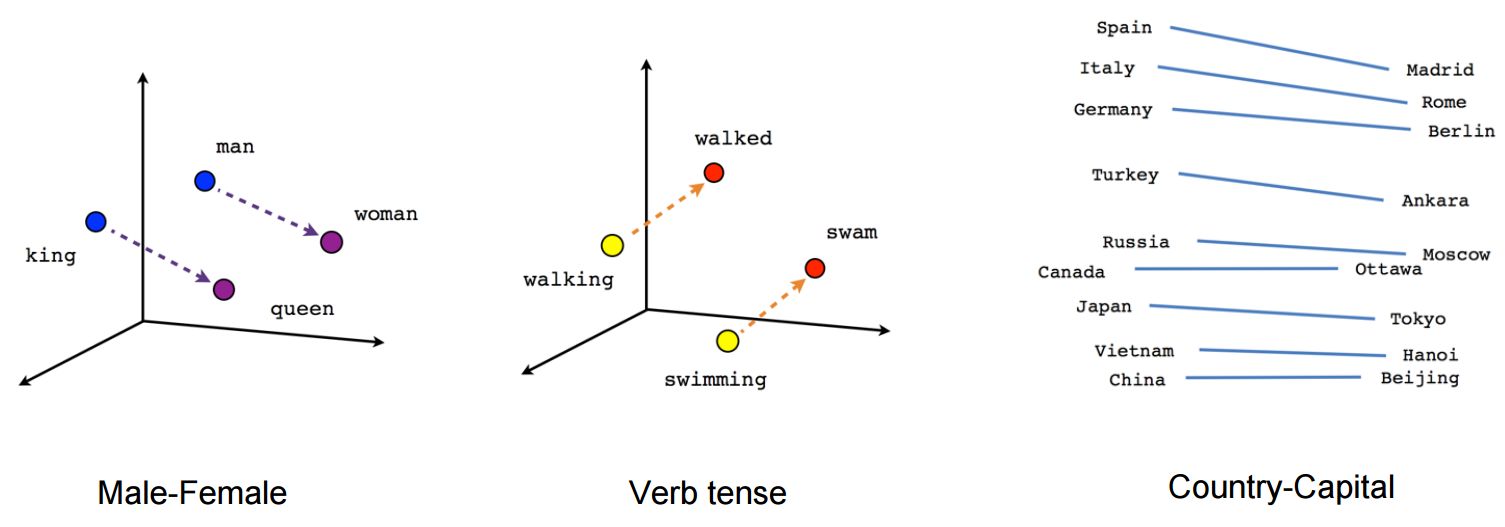
Semantic distance of similar words
France + capital = Paris
Germany + capital = Berlin
but still no context disambiguation: bank (river) = bank (finance), a play != to play, etc
word2vec 2013
Each word is a vector of large dimension
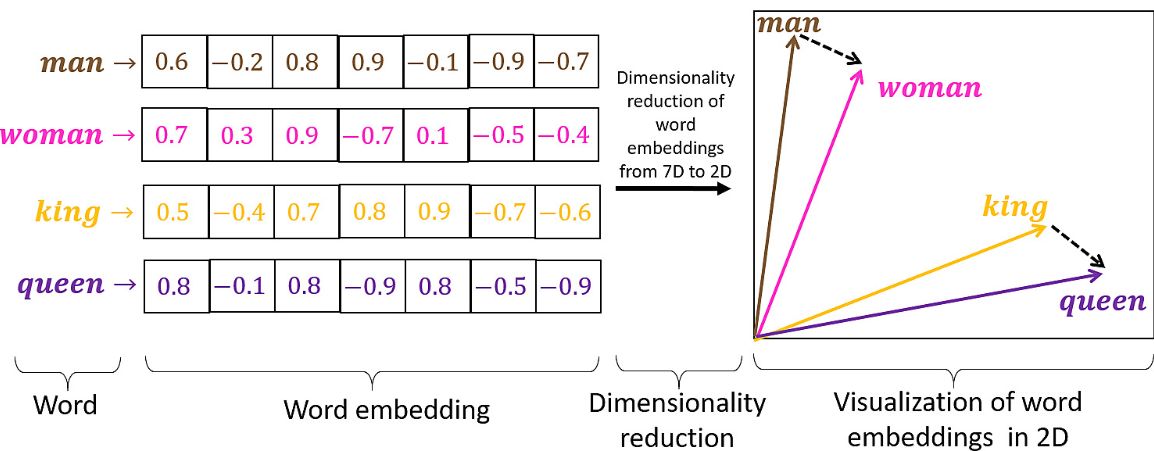
Vocab
Multi modal embeddings
Cosine similarity
Once you have embeddings (vectors, series of numbers) of 2 texts (sentences, words, tokens ,...), their distance is given by the cosine similarity of their embeddings
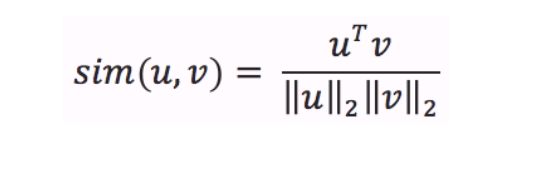
Example Workflow:
- Load a pre-trained embedding model.
- Pass your sentences through the model.
- Get a N-dimensional vector (embedding) for each sentence.
- Use these embeddings for your task.
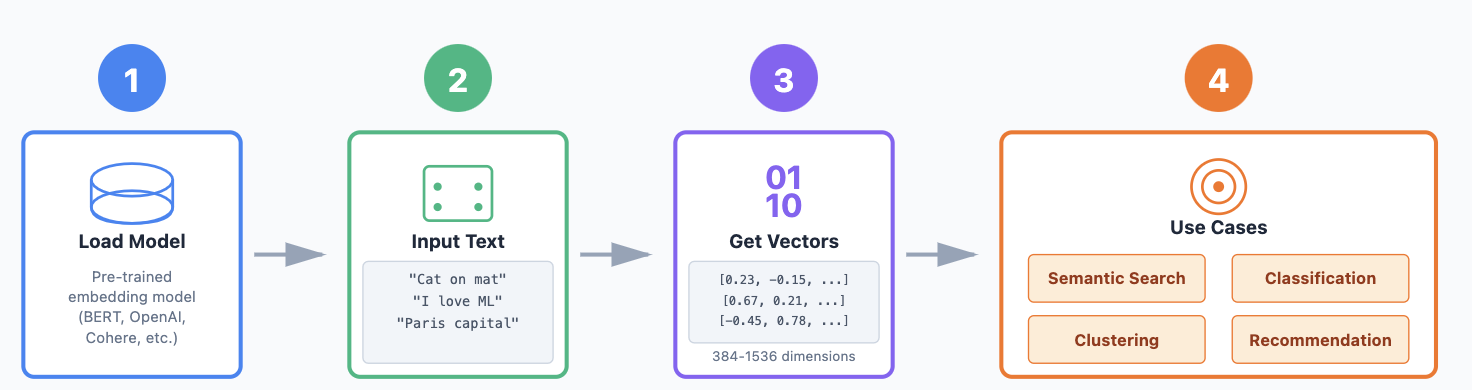
Specialized embeddings
Different companies optimize for different priorities—ease of use, multilingual support, domain expertise, or cost efficiency!
Leading Embedding Model Companies
OpenAI – Versatile, general-purpose embeddings
- Specialty: High-quality text embeddings that work across many domains
- Focus: Easy-to-use API, strong performance out-of-the-box
- Popular models: text-embedding-3-small, text-embedding-3-large
Cohere – Enterprise-focused, multilingual embeddings
- Specialty: Excellent semantic search and multilingual support (100+ languages)
- Focus: Business applications, RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation)
- Standout feature: Specialized embeddings for different use cases (search, classification)
Voyage AI – Domain-specific, customizable embeddings
- Specialty: Tailored embeddings for specific industries (finance, legal, healthcare)
- Focus: Highest accuracy through domain adaptation
- Approach: Fine-tuned models that understand specialized terminology
Jina AI – Multimodal and open-source embeddings
- Specialty: Text, image, and cross-modal embeddings
- Focus: Developer-friendly, customizable, cost-effective solutions
- Standout feature: Long-context embeddings (8K+ tokens)
Google (Vertex AI) – Integrated, scalable embeddings
- Specialty: Seamless integration with Google Cloud ecosystem
- Focus: Enterprise scale, multiple modalities
- Models: Gecko (text), multimodal embeddings
resources
- https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/embeddings
- https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/openai-embeddings
Core Architecture Comparison
| Word2Vec | Modern Methods (BERT/GPT) |
|---|---|
| Static embeddings | Contextual embeddings |
| One vector per word | Dynamic vectors per context |
| Same vector for "bank" | Different vectors per meaning |
| ~300 dimensions | 768-4096+ dimensions |
| Position-agnostic | Position encodings |
| Local context window | Full sequence attention |
Capabilities & Scale
| Word2Vec | Modern Methods (BERT/GPT) |
|---|---|
| Word similarity only | Multiple downstream tasks |
| Fixed vocabulary | Subword tokenization |
| No transfer learning | Pre-train + fine-tune |
RAG: Retrieval Augmented Generation
The LLM Context Limitation
Large Language Models have a context window—a limit on how much text they can process at once (typically 32K-200K tokens, or ~25-150 pages).
The Challenge:
- Your company has 10,000+ documents, millions of pages of data
- LLMs can't read everything at once—it won't fit in the context window
- Without the right information, LLMs either hallucinate or say "I don't know"
How RAG Solves This:
Before RAG: You ask: "What's our return policy for electronics?" LLM thinks: "I don't have access to this company's specific policies... I'll make an educated guess based on common practices" ❌
With RAG:
- Your question is converted to an embedding
- RAG searches through ALL your documents and retrieves only the most relevant 3-5 pages (your return policy docs)
- Those specific pages are inserted into the LLM's prompt as context
- LLM answers based on YOUR actual policy ✓
RAG acts as a smart search system that finds the needle in the haystack, then gives ONLY that needle to the LLM as context. This way, the LLM always has the right information to answer accurately—without needing to fit your entire knowledge base in its context window.
Bottom Line: RAG = Retrieval (find the right docs) + Augmented (add them to the prompt) + Generation (LLM creates answer from that context)
RAG : retrieval augmented generation

Main Challenges in RAG Systems
Chunking Issues
- Finding the right chunk size: too small loses context, too large dilutes relevance
- Poor boundaries break meaning (splitting tables, sentences, or code blocks)
Retrieval Quality
- Semantic mismatch: user words don't match document terminology
- Ranking failures: most relevant document doesn't make the top results
Version Control & Freshness
- Outdated documents remain in the vector database
- Multiple versions of same document cause conflicting answers
Context Limitations
- Retrieved content exceeds LLM's context window capacity
- Deciding which chunks to include when you have too many relevant results
Hallucinations Still Occur
- LLM extrapolates beyond retrieved documents
- Contradictory sources lead to invented compromises
Cost & Latency
- Re-embedding large collections is expensive
- Retrieval adds 2-5 seconds to response time
Intermission
Classic and modern NLP practice
On the wikipedia API
- Build a corpus on the wikipedia API
- split text into sentences (using spacy.io)
- Exctract Persons, Locations using NER (using spacy.io)
- for each sentence : get embeddings using huggingface transformers library
- find similar sentences from a key word or a query
- visualize with a graph
Colab
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1FT5hdlnj23c85CEYvaIc6nh4xDWu7VSW#scrollTo=cYFFIRy-6Ign
Practice
Load the dataset from the previous class into a pandas dataframe
-
extract all the NER in a new column
-
extract all adjectives or nouns in a new column
-
split the main text column into sentences
-
build a new dataframe with the sentences (keep some reference to the orginal datafarme)
-
using huggingface transformers library, build embeddings for each sentence
-
given a text (word, sentence, ...), find all the sentences that are most similar to it
Next time
- projects, troubleshooting
- LLMs
- Agents
new data source: Simon Willison
Exit ticket
