Getting data in the database and backups
plan
- demo on dumping a database (pgadmin, CLI)
- demo on restoring a database (pgadmin, CLI)
Then you will import the titanic dataset
- download the csv data file on your local
- create the database and the table
- import the data
- restore the database in that file either using pgadmin or CLI
in short
You cna use pgadmin or CLI to backup and restore your data
- you can either backup your data as a compressed dump file
- or you can dump the data as a SQL file
dump file
- you use pg_dump, pg_restore
pg_dump -U alexis -h localhost -p 5432 -f <path>/treesdb_backup.pg_dump postgres
pg_restore -U alexis -h localhost -p 5432 -d treesdb_backup <path>/treesdb_backup.pg_dump
SQL file
You execute the sql file with psql on a given database
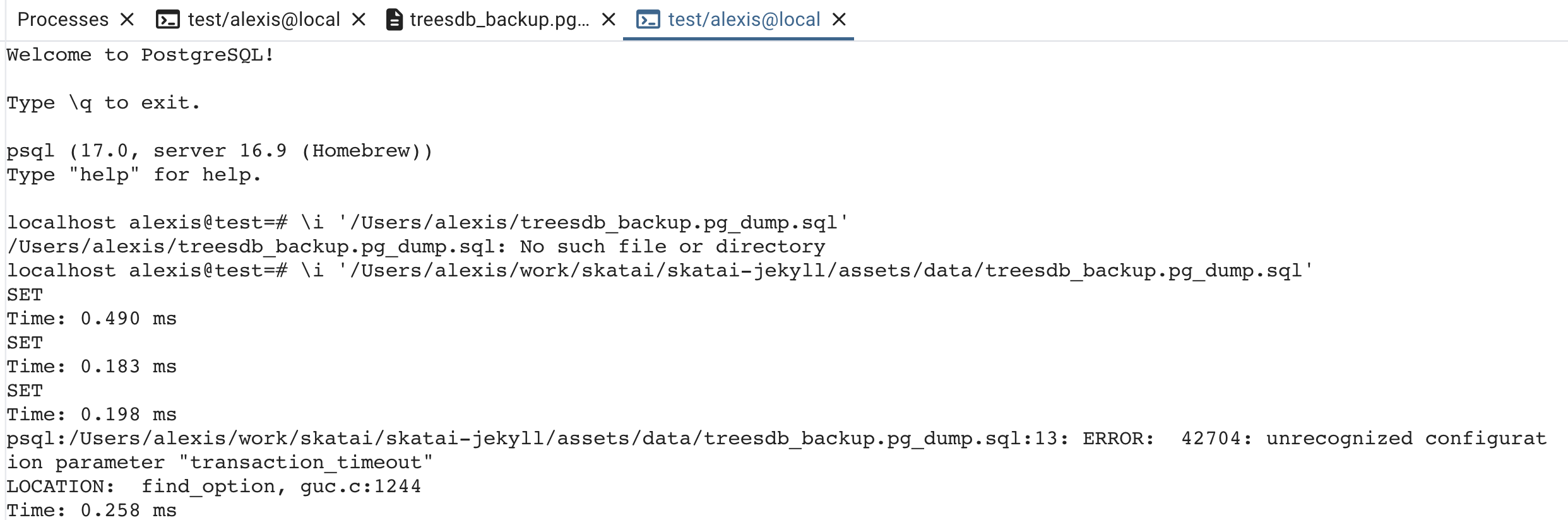
Demo : data backup
On my local, I have many databases
pgAdmin
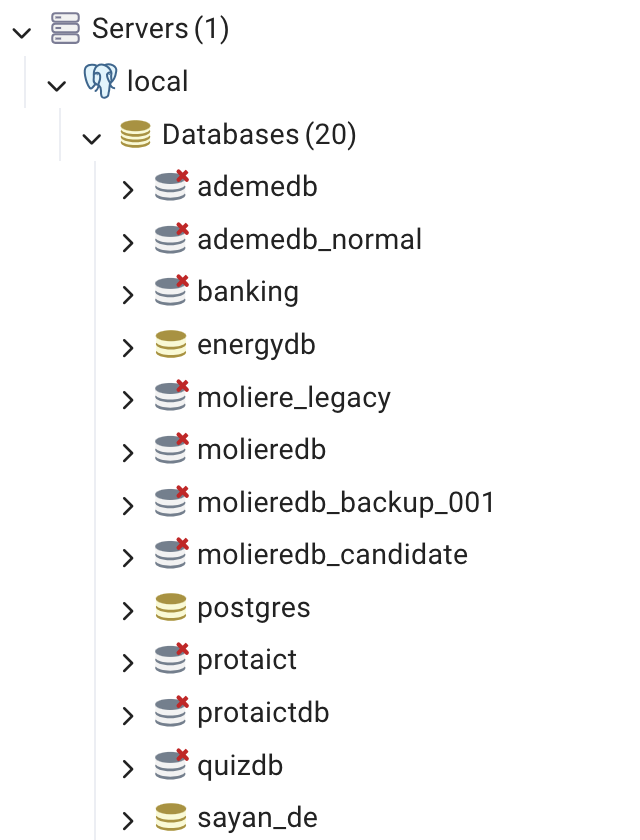
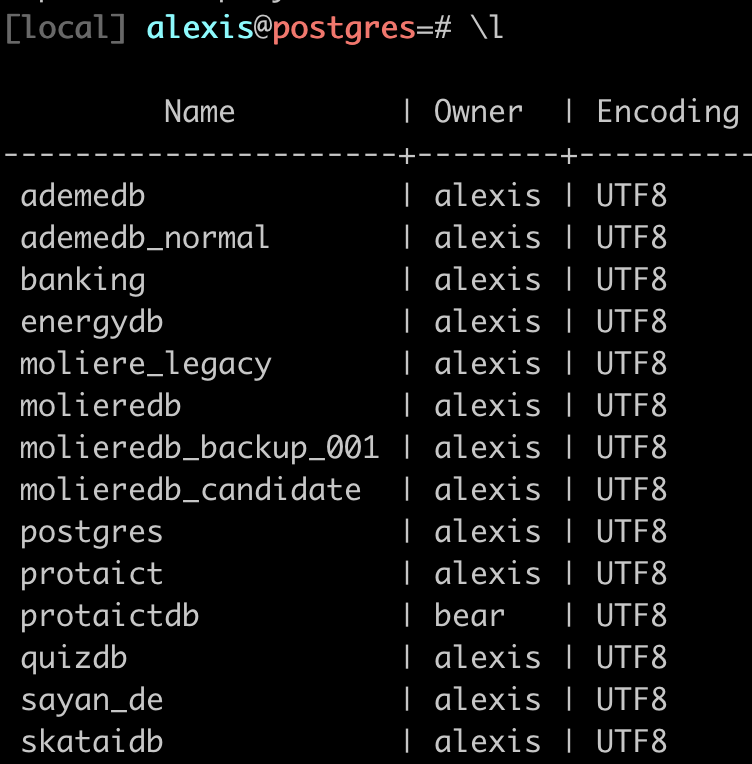
CLI : \l
Let’s back up one of these, for instance the treesdb_v01 database
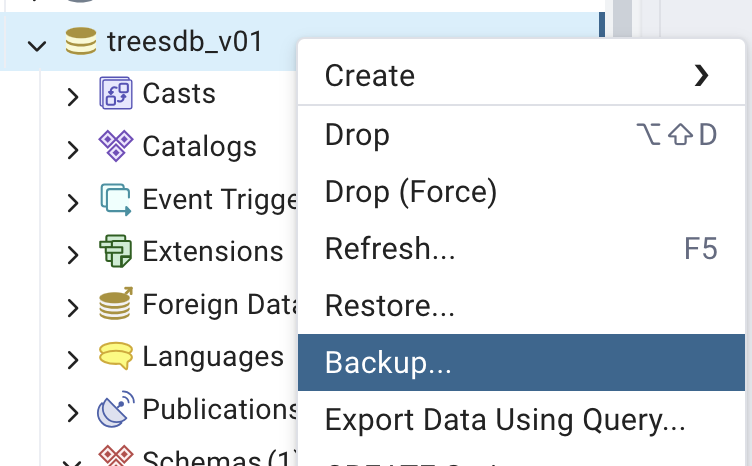
- Let’s name the backup file
treesdb_backup.pg_dump - Add a compression ratio from 1 to 9 (max) if you want to also compress your database. Then you should add
.gzto the filenametreesdb_backup.pg_dump.gzto indicate it is a commpressed file. - select
UTF-8for encoding. - for format : select plain (missing from the screenshot)
in the data options tab, select
pre data: includes the creation of the database and the userdata: includes the datablobs: includes all the data
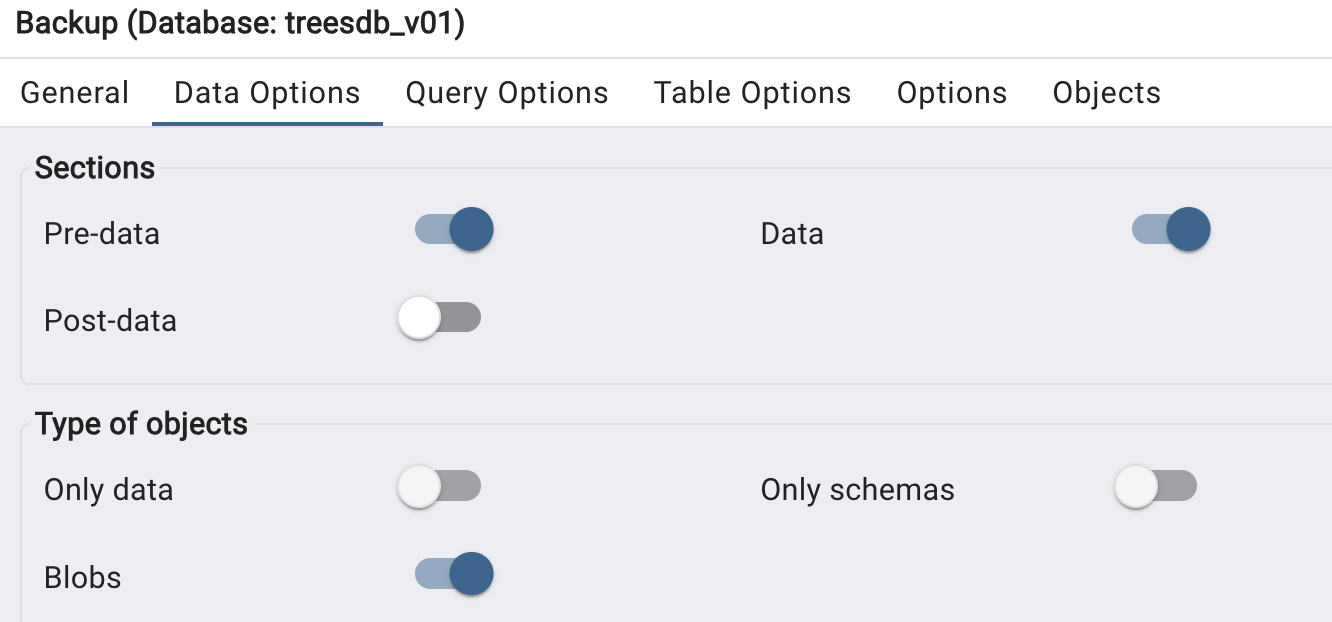
in the “Query Options section”, select
- include Create database
- include DROP database
- include IF EXISTS
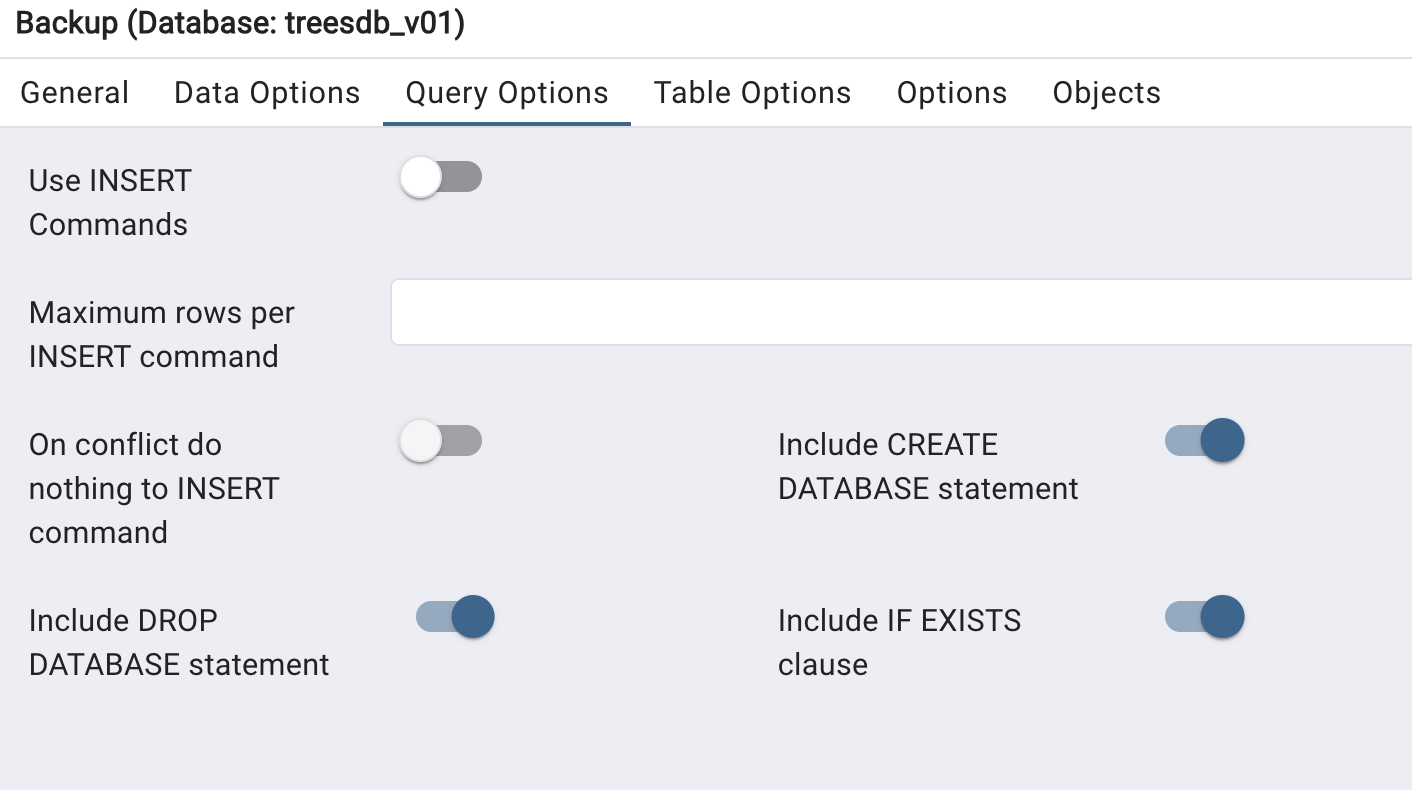
Nothing to do for the other tabs
and click Backup
Process
if we click on the process we see the CLI equivalent
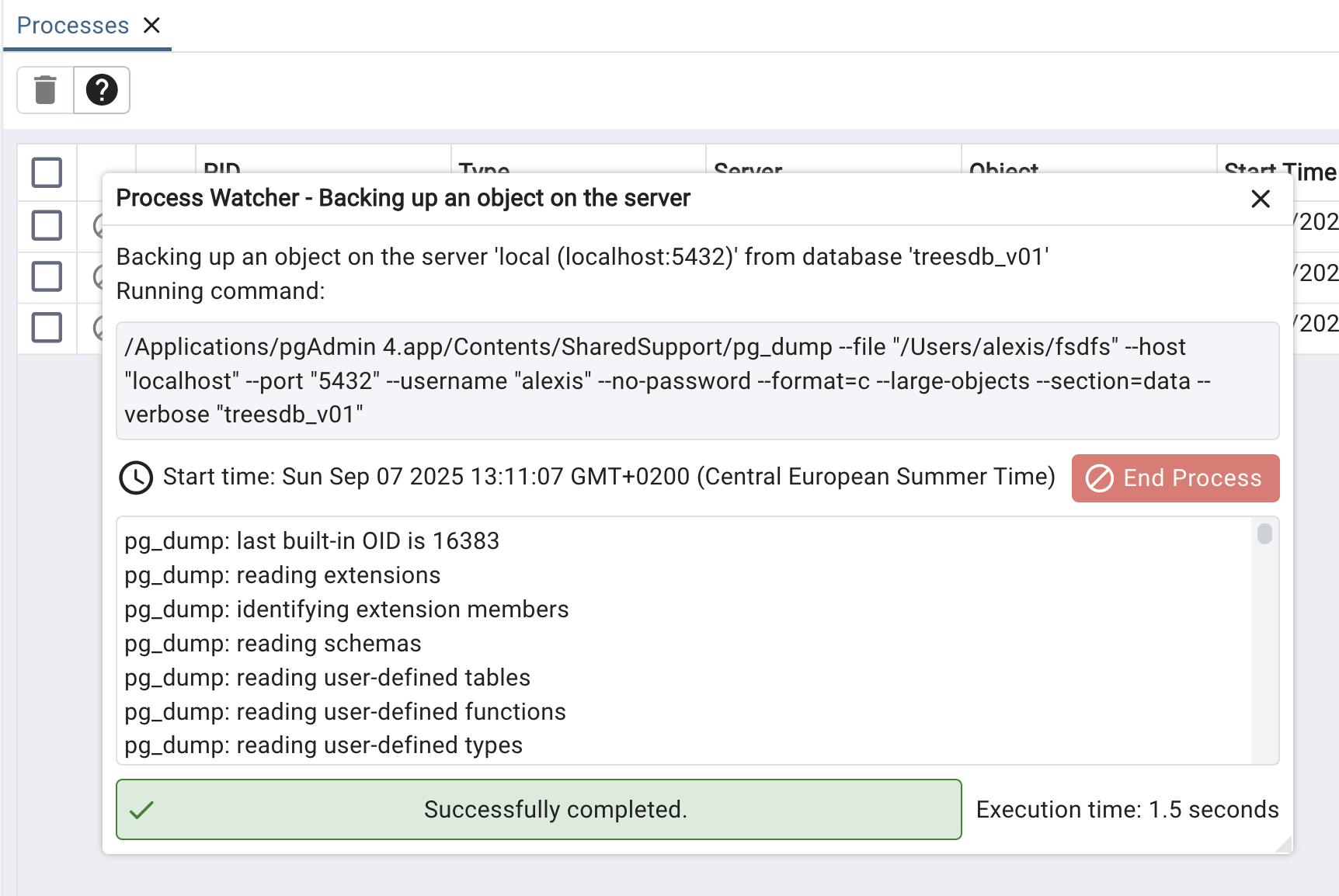
/<path>/pg_dump
--file "/Users/alexis/treesdb_backup.pg_dump"
--host "localhost" --port "5432" --username "alexis" --no-password
--format=p
--large-objects
--encoding "UTF8"
--section=pre-data
--section=data
--create
--clean
--if-exists
--verbose "treesdb_v01"
We can find all the settings that we selected in pgAdmin
I can copy paste that command into my terminal and it will / should work
Now let’s … restore
And restore it
Since the dump file is in plain text, it is just SQL statements that we can execute with psql.
psql -U alexis -h localhost -p 5432 -f <path>/treesdb_backup.pg_dump postgres
The -f simply says execute the file treesdb_backup.pg_dump.
Note
If I had used format=c (compressed) then to restore it I would have used pg_restore
pg_restore -U alexis -h localhost -p 5432 -d treesdb_backup <path>/treesdb_backup.pg_dump
✅ run a sql file In pgAdmin
First rename your file from treesdb_backup.pg_dump to treesdb_backup.pg_dump.sql
pgAdmin won’t open the file when it does not have the .sql extension
Then to run a dump file or any SQL file:
- Select a database (
postgresis fine) - Open the Query Tool on your server/DB.
- Go to the File icon / Open and select your
treesdb_backup.pg_dump.sqlfile. - The contents load into the Query Editor.
- Press the Execute (▶) button to run it.
This will execute the SQL statements in your dump (including CREATE DATABASE if you included it).
At this point you can simply use the PSQL tool in pgAdmin and run the above command
from now on, I will only use PSQL
The titanic dataset is a classic dataset used in machine learning competitions

A list of the 891 passengers with their survival status, age, sex, class, fare, etc.
The kaggle competition is to predict the survival of the passengers based on their features.
Here we will just load the dataset into a database and review some basic SQL queries.
The goal of the exercise is to be able to import any csv dataset into a database.
Titanic CSV fields are:
- PassengerId – integer, unique
- Survived – integer (0 = No, 1 = Yes)
- Pclass – passenger class (1, 2, 3)
- Name – passenger name
- Sex – male/female
- Age – float (because of decimals, and some NULLs)
- SibSp – number of siblings/spouses aboard
- Parch – number of parents/children aboard
- Ticket – ticket number
- Fare – float
- Cabin – cabin string, often NULL
- Embarked – port of embarkation (C, Q, S)
Steps
In order to import a csv file into a database
we will
- create the database
- create a simple table
- import the csv file into the table
Server vs Database vs Tables
- Postgresql runs on a server
- you connect to a database
- a database is a collection of tables
database creation
CREATE DATABASE titanicdb;
in pgAdmin, right click on Databases (n) and select Create Database
- add a name
- check out the SQL tab.
It will show the SQL command that will be executed
CREATE DATABASE titanicdb
WITH
OWNER = alexis
ENCODING = 'UTF8'
LOCALE_PROVIDER = 'libc'
CONNECTION LIMIT = -1
IS_TEMPLATE = False;
Note: it’s always good practice to name the database with a db postfix or prefix.
once the titanicdb has been created connect to it with
\c titanicdb
CLI
you can use the createdb command to create a database from the command line
createdb titanicdb
Create the table
CREATE TABLE titanic (
passenger_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
survived BOOLEAN,
pclass SMALLINT ,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
sex VARCHAR(10),
age REAL,
sibsp SMALLINT,
parch SMALLINT,
ticket TEXT,
fare NUMERIC(8,2),
cabin TEXT,
embarked CHAR(1)
);
where
- SERIAL is an auto-incrementing integer
- BOOLEAN is a boolean
- SMALLINT is a small integer
- TEXT is a text
- VARCHAR is a variable length string
- REAL is a real number
- NUMERIC is a numeric number
- CHAR is a character string
This is very precise. we could have used text for all strings and int / real for numbers
Note: there are no constraints on the table.
check
\d lists all the assets (tables, views, functions, etc.) in the current database
we have
localhost alexis@titanicdb=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+--------------------------+----------+--------
public | titanic | table | alexis
public | titanic_passenger_id_seq | sequence | alexis
sequence ?
Let’s check out the sequence
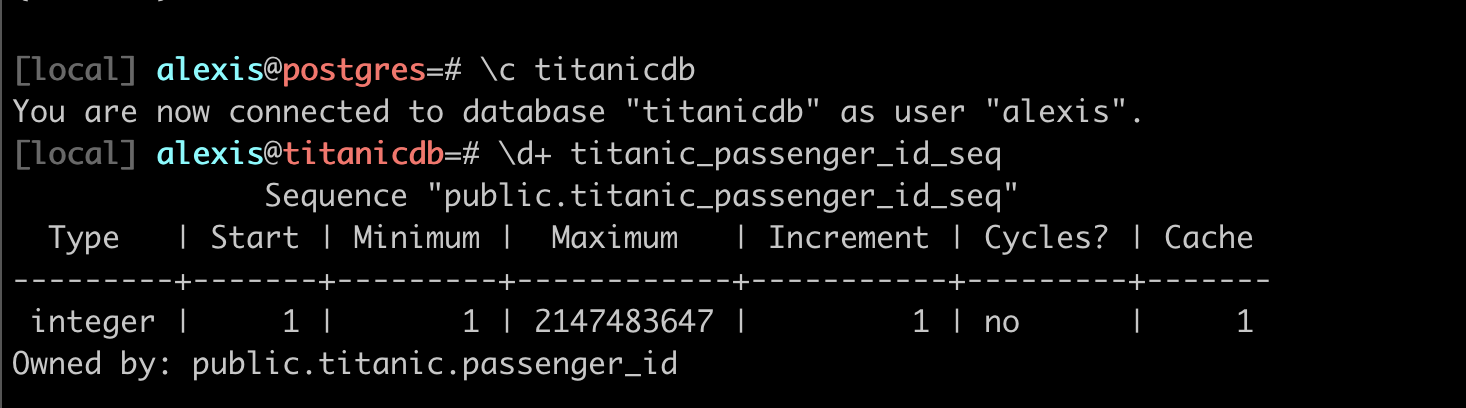
shows the behavior of the passenger_id serial number: from 1, increment 1, etc
Table
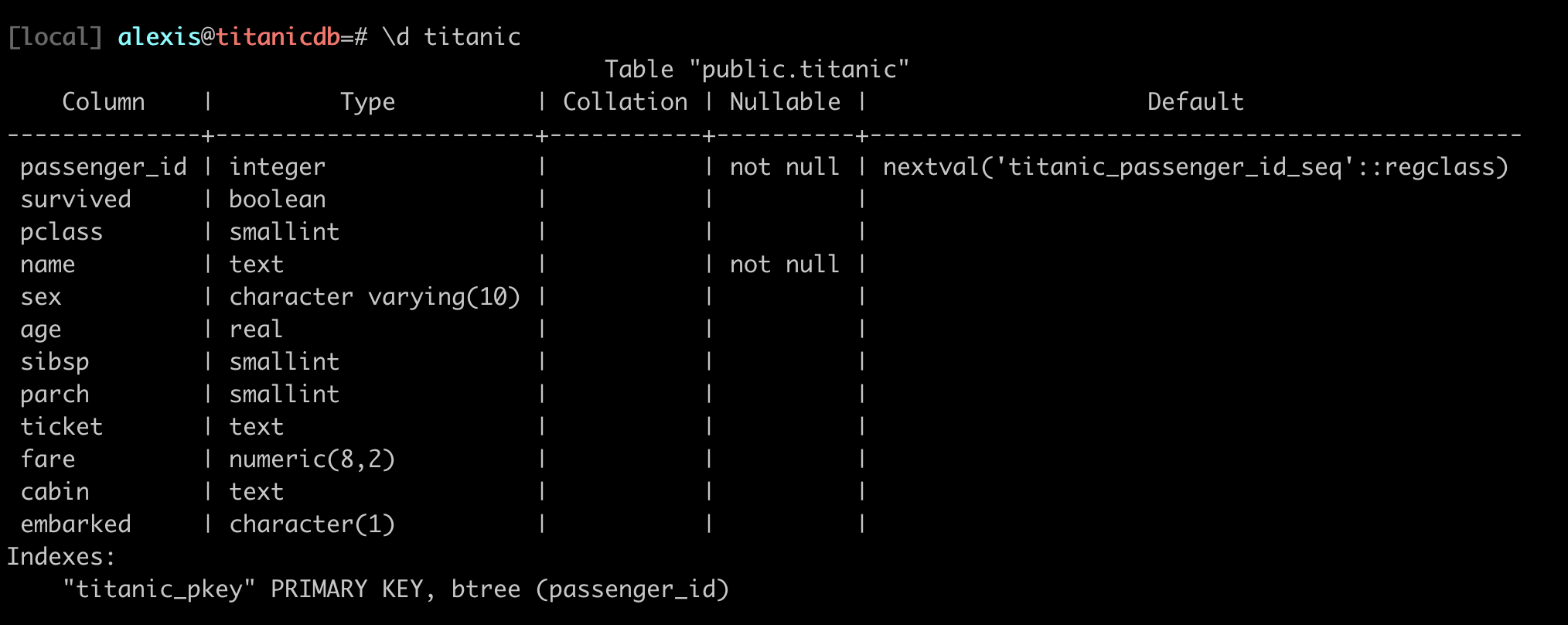
Notice in the last column.
nextval('titanic_passenger_id_seq'::regclass)
We can actually select the next value of the sequence
SELECT nextval('titanic_passenger_id_seq'::regclass);
Since our table is empty, this will return 1, then 2 etc
Import the csv data
Now to import the csv file into the table
COPY titanic FROM '/path/to/titanic.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
or
\copy titanic FROM '/path/to/titanic.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
There may be permission issues with the 1st COPY clause.
Note: you must use the absolute path to the file
if everything goes well you should have
COPY 891
and to verify this query should also return 891
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM titanic;
The CSV Import Challenge
Common Problems You’ll Face::
- 🔤 Character encoding (é, à, ñ, 中文)
- ❌ Missing values (empty cells, NULL, N/A)
- 📊 Wrong separators (
;instead of,) - 🔢 Type mismatches (“123” as text vs 123 as number)
- 📅 Date formats (DD/MM/YYYY vs MM/DD/YYYY)
Practice dumping and restoring the data
In pgAdmin or in the terminal
First backup the titanicdb database, without compression
- play with the options in pgAdmin: pre-data, data, post-data
- you will get a SQL file
- open the sql file in an editor and check the content.
- identify which part is the data and which part is the schema
- identify which part is the pre-data and which part is the post-data
Then
- create a new database titanicdb_restored
- restore the titanicdb database from the backup SQL file
Now dump the titanicdb database, this time with compression
You will get a pg_dump file
- dump the titanicdb database with compression
- restore the titanicdb_compressed database from the dump file
To finish, let’s practice some basic queries.