API
Application Programming Interface
What we saw last time
- open source vs closed source
- data sources
- data formats
- Project reviews
Any questions?
Today
- news review
- The web as a gigantic API
- the REST protocol
- inspecting a website (hack 101)
- building datasets from APIs
-
Project reviews
- Guided practice on the wikipedia API
At the end of this class
You
- understand what an API is
- know the 4 operations in the REST protocol
- can get data out of a public API
In the News
What caught your attention this week?
Claude can now edit files
https://www.anthropic.com/news/create-files
Qwen released 2 new models https://qwen.ai/blog?id=4074cca80393150c248e508aa62983f9cb7d27cd&from=research.latest-advancements-list
- Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct approaches our 235B flagship.
- Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Thinking outperforms Gemini-2.5-Flash-Thinking.
The name “80B-A3B” indicates 80 billion parameters of which only 3 billion are active at a time. You still need to have enough GPU-accessible RAM to hold all 80 billion in memory at once but only 3 billion will be used for each round of inference, which provides a significant speedup in responding to prompts.
More details from their tweet:
- 80B params, but only 3B activated per token → 10x cheaper training, 10x faster inference than Qwen3-32B.(esp. @ 32K+ context!)
- Hybrid Architecture: Gated DeltaNet + Gated Attention → best of speed & recall
- Ultra-sparse MoE: 512 experts, 10 routed + 1 shared
- Multi-Token Prediction → turbo-charged speculative decoding
- Beats Qwen3-32B in perf, rivals Qwen3-235B in reasoning & long-context
Ethan Mollick
- https://www.oneusefulthing.org/p/on-working-with-wizards from collaboration to conjuring.
Claude tools
In Claude:
Show me a list of tools that you have available to you, duplicating their original names and descriptions
Claude memory
https://simonwillison.net/2025/Sep/12/claude-memory/
API
An API defines
- the methods and data formats
- that applications can use
- to request and exchange information.
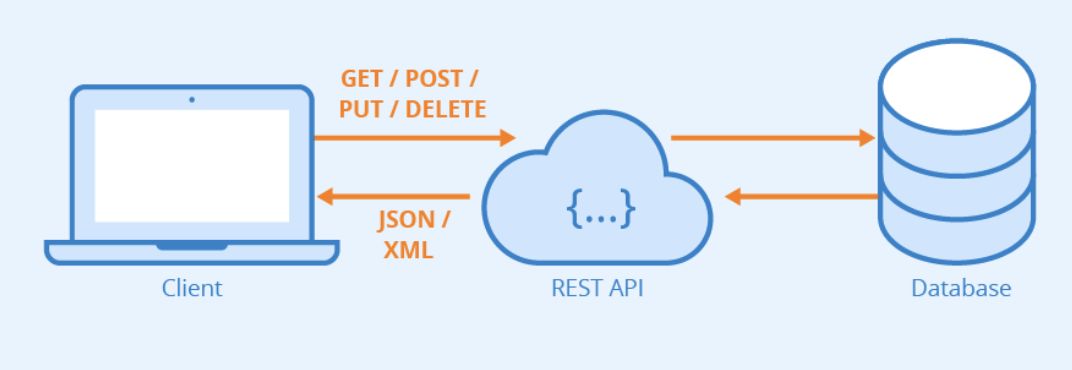
In other terms : an API allows apps to talk to each other.
API
- You send a request to a web address : a url
- The server answers the request
- You get back some data
Attention! - Attention!
In safari and other browsers, the full URL is hidden.
In the finder, go to settings » advanced
enable the “Show full website address” option.
What’s a URL ?
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address of a unique resource on the internet.
domain name + everything else to specify the data you requested
https://{domain name}/{endpoint}?{params}
Example :
https://skatai.com//inwai/api/#slide-9
REST protocol
The REST protocol is a set of rules that define how applications can interact with each other.
Four verbs to rule the world
- GET : read the data
- POST : create the data
- PUT : update the data
- DELETE : delete the data
The whole digital economy is based on these 4 words!
Example
- you read your feed: GET
- you like a post : POST
- you update your profile : PUT
- you remove a reel : DELETE
example on instagram, bluesky, X, facebook, tiktok, etc.
and every other website
The Web is One BIG API + GET requests
- on your browser you go to a url. This is the initial GET request
- that request triggers a call to the server.
- the server sends you back the content as the response, most often as JSON
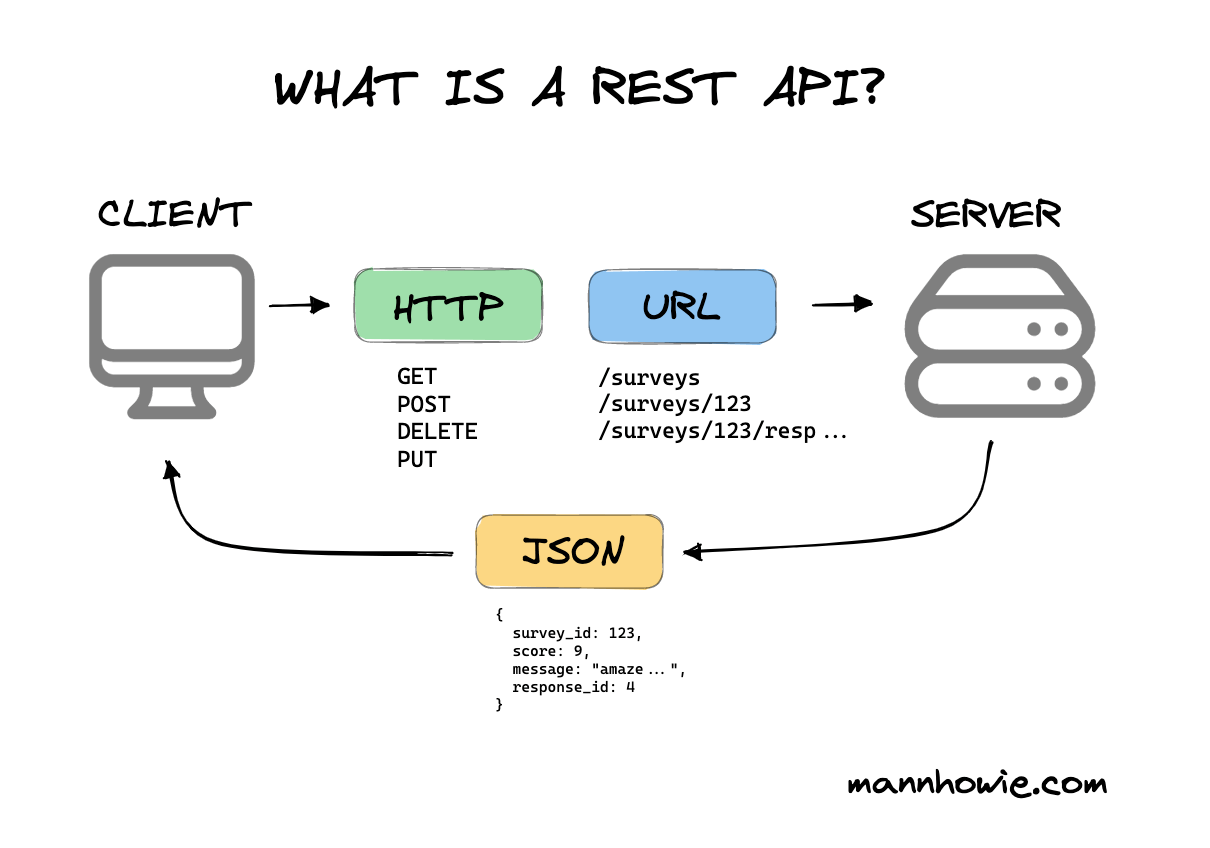
The Web is an API
Let’s illustrate
The web is one gigantic API
It uses URLs to send requests to a server
The server sends the html page back
- Go on goodreads.com
- Search for Dune
- Click on the author’s name Frank Herbert
You should end up on this URL:
https://www.goodreads.com/author/show/58.Frank_Herbert
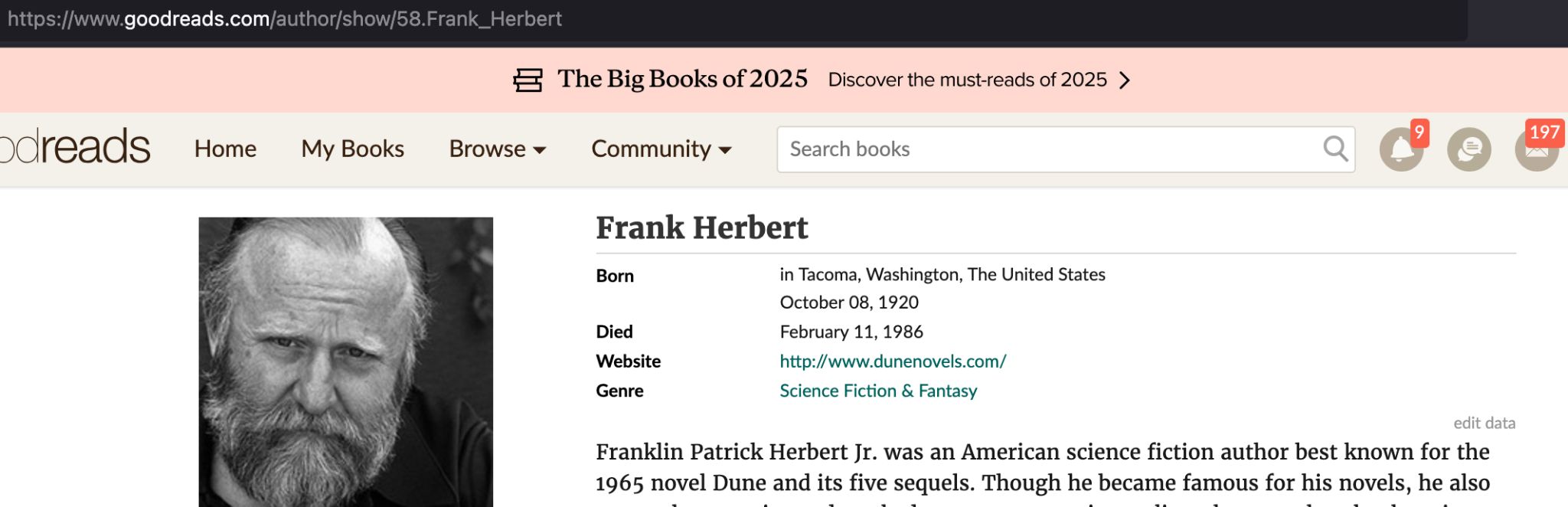
https://www.goodreads.com/author/**show**/58.Frank_Herbert
which can be read as: show an author, with label 58.frank.herbert
/list instead of /show
Now scroll down and click on “More Books by Frank Herbert”
The URL is now https://www.goodreads.com/author/list/58.Frank_Herbert
The verb “/show” is replaced with the verb “/list”.
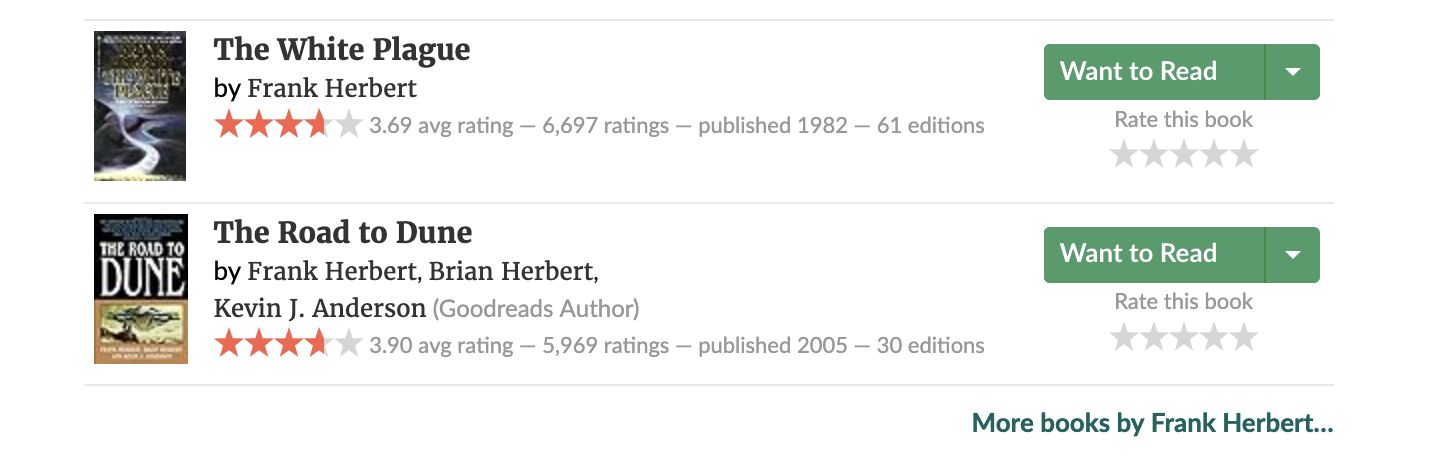
Parameters: ?page=2&per_page=30
Now click on page 2, the URL becomes
https://www.goodreads.com/author/list/58.Frank_Herbert?page=2&per_page=30
which reads
- list all the works of author 58.Frank_Herbert
- show page 2
- and show only 30 works per page
REST is the building block of the internet
An endpoint: an URL and a path
some optional parameters: ?page=2&per_page=30
A method : GET the content, PUT or POST new content, DELETE the content
The data in JSON format as the server response, or just plain text, html, pdfs, csv, audio, video etc
Examples
- Checking your Instagram story views → GET
- Looking at someone’s LinkedIn profile → GET
- Checking your bank account balance → GET
- Creating a new Spotify playlist → POST
- Sending a tweet → POST
- Adding a new card to Apple Pay → POST
- Changing your Discord status → PUT
- Viewing your Uber ride history → GET
- Canceling a Netflix subscription → DELETE
- Unlike a post → DELETE (removing the “like” record)
- Liking someone’s post → POST (creating a new “like” record)
- Refreshing your email inbox → GET
quizz
For each action, guess which REST verb it uses: GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE?
- Checking your train schedule →
- Removing an item from your online shopping cart →
- Booking a hostel for your trip →
- Looking up a word in an online dictionary →
- Submitting an assignment on Moodle/Canvas →
- Checking the weather forecast →
- Changing your delivery address for an order →
- Viewing your grades online →
- Deleting an email from your inbox →
- Modifying your alarm time →
- Checking your library book due dates →
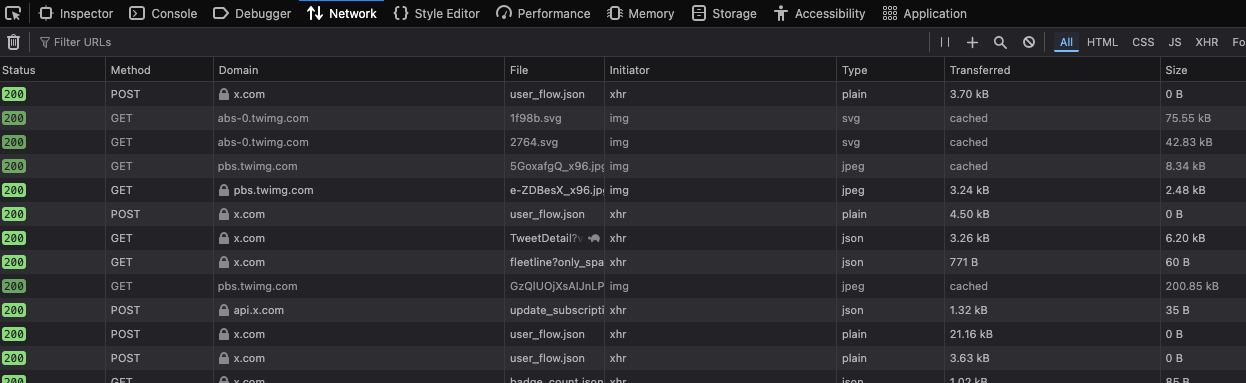
Hack 101
DEV tools - under the hood
go on a social network or a website
- click right and get to the developpers tools : inspect
- click on network tab
- like a post: you should see a request with method POST
- click on a post: you should see a requests with method GET
Exercise
Grab a screenshot of the Devtools screen, network tab
Paste in a LLM like chatGPT or Claude or …
ask: explain in simple terms what I’m seeing
Wikipedia API

The wikipedia API
We can use the API front end (sandbox) to play with the API but as we can see it’s not trivial
- The sandbox : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special:ApiSandbox
So we need to read :
- The API documentation https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/API:Main_page
Best to check out
- The wikipedia python library: https://wikipedia.readthedocs.io/en/latest/code.html
# Do a Wikipedia search for query.
wikipedia.search(query, results=10, suggestion=False)
read the docs
Install the library
First install the library : !pip install wikipedia-api
Note the ! before pip.
Then we look at some code
prompt : PIP Install the wikipedia api library
import wikipediaapi
# Initialize Wikipedia API (English)
wiki_wiki = wikipediaapi.Wikipedia( user_agent="[email protected]", language='en')
# Get the page : the actual request to the API
page = wiki_wiki.page("Paris")
# Check if the page exists
if page.exists():
print(f"Title: {page.title}\n")
print(f"Summary: {page.summary[:500]}...") # print first 500 chars of summary
else:
print("Page not found.")
instanciate the object
pass all the parameters to specify how how want to interact with the object
wiki_wiki = wikipediaapi.Wikipedia( user_agent="[email protected]", language='en')
wiki_wiki is the object that we use to interact with the API. It has now been initialized, or instanciated
to interrogate APIs you often also have to pass all the required identification parameters (login, password, API key, …). This is not needed for wikipedia API. The wikipedia API is 100% open.
strings
- Simple, direct
print("Hello world")
- With a variable
my_var = "Hello world"
print(my_var)
- interpolation
f-strings
my_var = "Hello world"
print(f"Greetings: {my_var}")
notice :
- the
fbefore the string - the
{}around the variable
multiple variables
my_var = "Hello world"
name = "Alexis"
print(f"Greetings: {my_var} \n my name is {name}")
Notice
- the
\n. \nis the line return character
Practice
- Print the string
"My name is Spiderman" - Create a variable called
herowith the value"Spiderman" - Print the variable
hero - Print
"Hero:"followed by the variablehero(concatenation) - Create another variable
quote = "With great power comes great responsibility" - Print using an f-string “hero says …
"
Methods vs attributes
we’ve seen that with pandas dataframes : df.head() vs df.columns
A method / function call : notice the presence of absence of ()
page.exists()
A property on the object page: no ()
page.title
practice
Full worksheet : wikipedia api practice
short version:
- use the wikipedia API to get a page (for instance a city, a person, a country)
- explore what available elements the
pageobject has besides title and summary - create an array of similar pages (
["Paris", "New York", "Tokyo", "London", "Berlin"]) - use the wikipedia API to get the summary of each page
- print the summary of each page
- store the pages in a pandas dataframe with columns : url, title, summary
- store the dataframe in a csv file on your local machine
Next time
- more python
- NYT API
- NLP
- Spacy
new data source: aifray.com
In-depth reporting and analytical commentary on artificial intelligence regulation.

